Invasive species in a changing climate
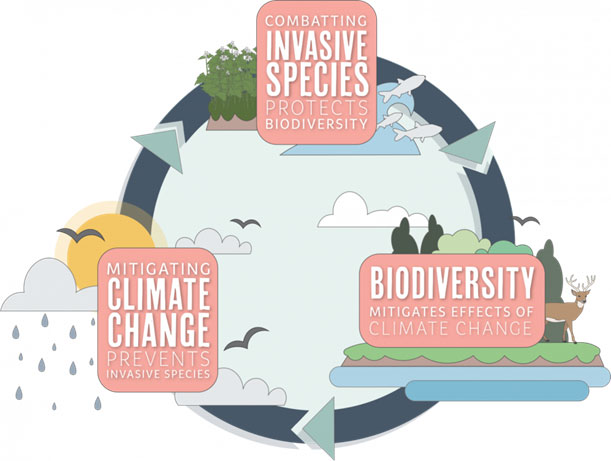
Climate change can accelerate the introduction and spread of invasive species. Together, invasive species and climate change reduce ecosystem resilience and negatively impact biodiversity.
Effects of climate change on invasive species can include:

More frequent extreme weather events (such as floods and droughts) stress native species and create opportunities for invasive species movement.

Melting sea ice opens new shipping routes and pathways for invasive species spread.
A changing climate can affect species life cycles and their ability to spread into new areas.

Increased carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere leads to higher CO2 uptake in plants, which can increase herbicide resistance.
Changes to climate (including temperature, humidity, and rainfall) can create favourable conditions for increased spread of invasives.
Sleeper species
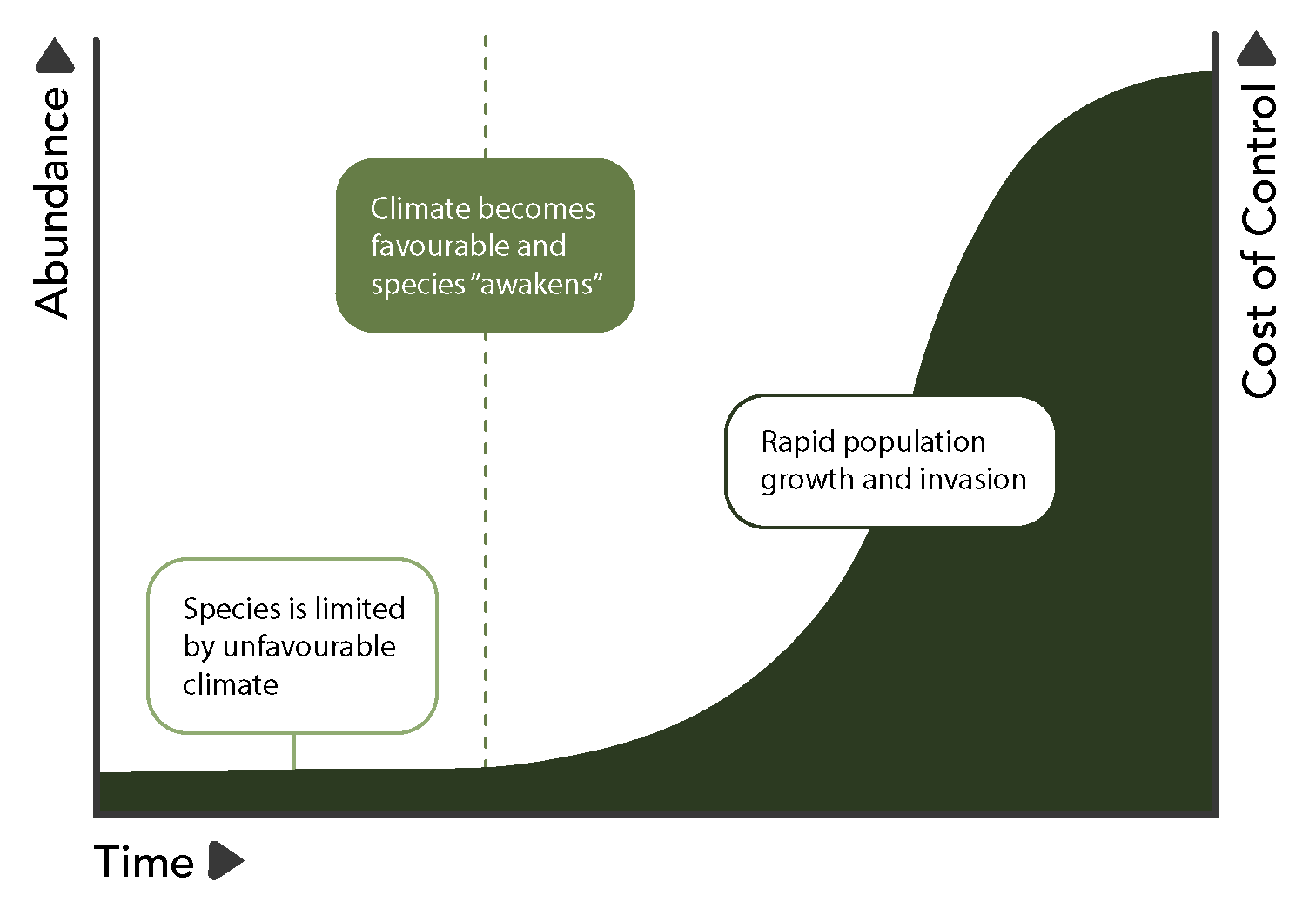
Sleeper species are non-native species already present in an ecosystem that have potential to be invasive, but are limited by factors such as climate or other species.
Sirex woodwasp, for example, was introduced to Canada in 2005 and has since been limited to parts of Ontario and Quebec. Climate change could create favourable conditions for the spread of this species, leading to negative impacts on Canada’s important pine plantations. Identifying sleeper species and preventing their spread will protect vulnerable ecosystems and maximize resources.
Graphic adapted from Bradley et al., 2018.
Case study: Mountain pine beetle
Mountain pine beetle (MPB;
Dendroctonus ponderosae) is native to Western Canada, but has rapidly spread beyond its historical range in recent years. Warming winters have enabled spread into areas where the cold previously killed up to 98% of populations. MPB is now acting ‘invasive’ and threatens pine trees across Canada.
Healthy forests are carbon sinks that capture and store large amounts of atmospheric carbon and help offset the impacts of climate change. A MPB outbreak could turn Canada’s forests from a carbon sink to a carbon source, as killed trees release stored carbon back into the atmosphere – further accelerating climate change.
What can we do?
- Incorporating biosecurity, early detection, and rapid response in climate change policy will help prevent the introduction and spread of invasive species.
- Ecosystems that are already impacted by invasive species should be prioritized for management to improve the resilience of our natural environment.
- The spread of invasive species weakens ecosystems and makes them more vulnerable to the effects of climate change. By preventing the spread of invasive species, we also protect our natural environment from the effects of climate change.
Resources

Invasive Species and Climate
Change Fact Sheet
Further Reading
IUCN – Invasive alien species and climate change
University of Massachusetts Amherst – Regional Invasive Species & Climate Change Management
